| Air |
| WATER |
|
| SOLID WASTE |
| AGRICULTURE |
|
| CLIMATE |
| DEMOGRAPHY |
| BIODIVERSITY |
|
|
|
 |
| Save Ganga Save Dolphin |
|
|
Economy of Bihar |
| |
General Overview |
Bihar, is located in the eastern part of India and is bounded by West Bengal in the east, Uttar Pradesh in the west, Himalayan mountain range in Nepal in the north and by Jharkhand in the south. The capital of Bihar is Patna. It is an entirely land–locked state, although the outlet to the sea through the port of Kolkata is not far away. The Bihar plain is divided into two unequal halves by the river Ganga which flows through the middle from west to east. Bihar lies mid-way between the humid West Bengal in the east and the sub humid Uttar Pradesh in the west which provides it with a transitional position in respect of climate, economy and culture.
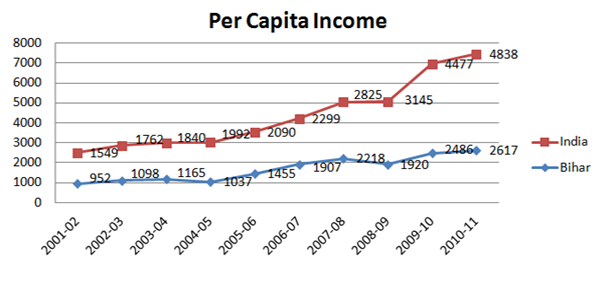
The economy of Bihar is largely service oriented, but it also has a significant agricultural base. The state also has industrial sector. As of today, agriculture accounts for 35%, industry 9% and service 55% of the economy of the state. There is virtually no manufacturing sector in Bihar but its share is increasing.
Construction sector is growing exponentially and it is a important part of the state’s economy. Its share in GSDP has increased from 3.8% to 12.15% over last ten years. Construction sector seems to be immune to volatility in agricultural or even overall economy. It continues to grow apace even in the worst years of recession. Trade, Hotels and Restaurants are another major component of state’s economy that has seen rapid growth (12%/year) over the last decade.
|
Agriculture |
Bihar lies in the Indo-Gangetic plain and its fertile farmlands grow maize, rice, barley, ragi, pulses and wheat and cash crops like potato, sugarcane, jute, onion, chillies, mesta, tobacco and oil seeds. The state also grows litchis, mangoes, banana and jackfruit. Bihar accounts for 65 per cent of India's annual litchi production; it has significant level of production for vegetables like brinjal, tomato, cauliflower, bhindi, and cabbage in the country and having leading role in food production also. It is also particularly rich in water resources. The Ganga is the biggest river to flow through Bihar; other major rivers include Gandak, Ghaghra, Kosi, Bagmati and Mahananda. While these are invaluable for irrigation and may be tapped to produce hydroelectricity, they also cause great havoc annually when large parts of Bihar get flooded. Bihar also has great forest resources. |
Energy |
Energy plays a vital role in the socio-economic development and human welfare of a state. Earlier, Bihar was amongst India's most backward states in terms of power development but situation of power availability in the state is improving fast. |
Current Electricity Scenario in Bihar
Attribute |
Value |
Total Demand |
3500 MW |
Total Availability of Power from all its Sources |
|
Power Supply to Emergency Services |
337 MW |
Power for Civil Supply |
|
Sources of Power |
Supply from Central Allocation |
1726 to 1772 MW |
State own Installed Capacity(Barauni & Muzaffarpur) |
Generation by Bihar State Hydroelectric Power Corporation Limited . |
55.1MW (Operational) & 34.3 MW
(Under Construction) |
Per Capita Consumption |
|
|
An allocation of 660MW from stage-II of the NTPC's Barh thermal power station has been promised to Bihar by the central agencies. A number of Solar Power Projects, located in several districts of state, are in progress. NPCIL proposed for installation of 4x700 MW Nuclear Power Plant at Rajauli, Dist.- Nawadah. |
Industry |
Bihar has Oil refinery of Indian Oil Corporation at Barauni, Super Thermal Power Projects at Kahalgaon, Bhagalpur and Barh (in District-Patna); 11 sugar mills and 7 distilleries units in private sector located in Gopalganj, West Champaran, East Champaran, Samastipur and Riga (District- Sitamarhi); finish leather industry in Muzaffarpur; Jute mills at Katihar and Samastipur; Food processing units and Vanaspati manufacturing units at Aurangabad and Patna; Kalyanpur Cement Ltd at Banjari in District-Rohtas are some of the notable industries in Bihar. In addition, State’s power plants at Barauni and Kanti, Muzaffarpur. A number of thermal power plants are in pipeline located in Bhagalpur, Aurangabad, Lakhisarai, Banka and Buxar. There have been attempts to industrialize the state. |
Forest Cover |
Forestry and wildlife are an important component of Bihar economy. Forest covers around 6.87% of the total geographical area of Bihar. Forestry of Bihar have contributed wood and various other raw materials of good quality which has made the state to earn good revenue. Out of the total land area, 3,208.47 km2 of land in Bihar falls under the protected forest area and located in West Champaran, some parts of Darbhanga, Jamui, Nalanda and Rohtas. |
Soil |
Soil is one of the most important resources of a nation. It is the gift of nature of immense value. The most common use of the word soil is in the sense of a medium in which plants grow, although it has a different connotation at different time and place, and for persons engaged in different professions. Almost all the economic activities are directly or indirectly dependent on soil. Thus soil is the backbone of agricultural and industrial development. Soil has a number of characteristics, which may be regarded as the aggregate of the physical, chemical and biological properties.
There are three major types of soil in Bihar:
Piedmont Swamp Soil - found in northwestern part of west Champaran district;
Terai Soil – found in northern part of the state along the border of Nepal; and
The Gangetic Alluvium – the plain of Bihar is covered by gangetic alluvium (both new as well as old).
|
Land Utilization Pattern (2009-10)
Total Area |
93.60 lakh Hec. |
Forest |
6.22 lakh Hec. |
Barren and Non-Cultivable Land |
4.32 lakh Hec. |
Land put to Non-Agricultural uses |
16.90 lakh Hec. |
Culturable Waste-land |
0.45 lakh Hec. |
Permanent pasture & grazing land |
0.16 lakh Hec. |
Miscellaneous tree crops and groves |
2.44 lakh Hec. |
Other fallow land (2 to 5 years) |
1.22 lakh Hec. |
Current fallow |
8.58 lakh Hec. |
Net Area Sown |
53.32 lakh Hec. |
Total Cropped Area |
72.96 lakh Hec. |
Area sown more than once |
19.64 lakh Hec. |
|
Rivers |
Bihar is richly endowed with water resources – ground and surface water; the Ganga is the main river which is joined by tributaries with their sources in the Himalayas; some of the other rivers are Saryu, Gandak, Budhi Gandak, Bagmati, Kamla and Mahananda |
Mineral Resources |
Minerals like Limestone, Silica Sand, Soap Stone, Stone, Sand, Boulder, Morram and Quartzite are found in abundance in Bihar |
Key Bihar Statics |
Latitude |
24°-20'-10" ~ 27°-31'-15" N |
Longitude |
83°-19'-50" ~ 88°-17'-40" E |
Rural Area |
92,257.51 sq. kms |
Urban Area |
1,095.49 sq. kms |
Total Area |
94,163.00 sq. kms |
Height above Sea-Level |
173 Feet |
Normal Rainfall |
1,205 mm |
Avg. Number of Rainy Days |
52.5 Days in a Year |
Population |
10,38,04,637 |
Male |
5,41,85,347 |
Female |
4,96,19,290 |
Length of National Highway |
3,734.38 km |
Length of State Highway |
4,857.00 km |
Length of Major District Roads |
9,030.00 km |
Length of Rural Roads |
20.190.00 km |
Village Roads |
67,810.00 km |
No of Airports |
2 |
|
 |
Economy Survey |
Download in English |
Download in Hindi |
Economic Survey of Bihar 2013-14 |
 |
 |
Economic Survey of Bihar 2012-13 |
 |
 |
Economic Survey of Bihar 2011-12 |
 |
 |
Economic Survey of Bihar 2010-11 |
 |
 |
|
|

